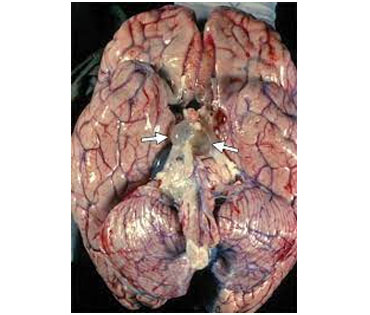
Neurocysticercosis is a neurological disease that occurs when a particular type of parasitic tapeworm invades the central nervous system.
Neurocysticercosis is the most common parasitic infection of the central nervous system (CNS).
The disease affects people who ingest the tapeworm Taenia solium, and it developsTrusted Source when the worm’s larvae build up in the muscles, eyes, skin, and CNS.
Diagnosis
Neurocysticerosis is diagnosed by computed tomography (CT) scan.[3] Diagnosis may be confirmed by detection of antibodies against cysticerci in CSF or serum[5] through ELISA or immunoblotting techniques.
Treatment
Treatment of neurocysticercosis includes epileptic therapy and a long-course medication of praziquantel (PZQ) and/or albendazole.[3] Steroid therapy may be necessary to minimize the inflammatory reaction to dying cysticerci.[6] Surgical removal of brain cysts may be necessary,[6] e.g. in cases of large parenchymal cysts, intraventricular cysts or hydrocephalus
Albendazole has been shown to reduce seizure recurrence in those with a single non-viable intraparenchymal cyst.[8] For seizures further randomized controlled trials are needed to evaluate the efficacy of antiepileptic drugs (AED) for seizure prevention in patients with symptoms other than seizures and the duration of AED treatment in these cases.